 Share Your Requirements
Share Your Requirements
Do you run a business or a startup? And do you want to make sure your ideas, brand, and creations stay yours? If the answer is yes, then there's no doubt about it: understanding IP Protection rights (Intellectual Property Rights) is a must. Think of your brand, your ideas, and your unique creations as your business's superpowers. Isn't it like it, so precious and a testament of your pure hard work, time and efforts. But, without the right shield, anyone could take them. In today's fast-moving digital world, strong IP protection is your best defense, keeping your content, inventions, and brand identity safe from being copied or misused. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), the global IP filings reached 16.5 million trademark applications and 3.5 million patent applications in 2023. It underscores the importance businesses place on securing their intellectual assets. And that, many business owners already know this. Yet, many business owners remain unclear about the differences between copyright vs trademark vs patent , often leaving valuable assets vulnerable.
Your brand, innovative ideas, and unique creations is truly like a goldmine of your company. Therefore, this blog guide provides a clear, fact-backed words to help you understand which type of IP protection is right for your business, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.
Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind such as inventions, designs, written works, and brand identifiers. These intangible assets often represent a large portion of a company's value. According to the Ocean Tomo 2020 study, intangible assets now account for 90% of the S&P 500's market value, highlighting the business-critical nature of IP management.
While copyrights, trademarks, and patents are all IP rights, they each protect different aspects of a business's work. Choosing the right one ensures you are legally covered and can take action against infringement.
Defintion: Copyright protects original works of authorship including literary, artistic, musical, and certain intellectual works from being copied or used without permission. A copyright protects the expression of an idea, not the idea itself. In software, this applies to the code and the user interface. It grants the creator the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and display the work.
Example:
1. If your business produces a custom software application, copyright ensures that your competitors cannot replicate or distribute the code without your consent.
2. The specific code written for a new accounting software is protected by copyright. If another company copies that code, it is a copyright infringement. The unique arrangement and layout of the software's user interface (UI) is also protected.
Want to read about? Intellectual Property Protection for Source Code | A Developer's Guide
Definition: A trademark protects brand identifiers such as names, logos, and slogans that differentiate your goods or services from competitors. A trademark protects brand identifiers such as a name, logo, or slogan. It distinguishes the goods and services of one company from those of others.
Example:
Definition: A patent protects new inventions and innovations, giving the inventor exclusive rights to produce, use, and sell the invention for a fixed period. It protects new and non-obvious inventions. This includes a new process, machine, or a method. For software, patents often cover the functionality or algorithm that makes the software innovative.
Example:
1. Dyson's cyclone vacuum technology is patented, preventing other companies from copying its unique design and mechanism.
2. A new, efficient algorithm that processes financial data in a unique way within the accounting software could be patented. This prevents other companies from using the same method, even if they write their own code for it.
You may also like | Why Every Business Needs Strong IP Protection
Copyright vs Trademark vs Patent explained for businesses, protect your ideas, brand, and innovations with the right form of legal IP protection rights. Under their differences well with below infographic.
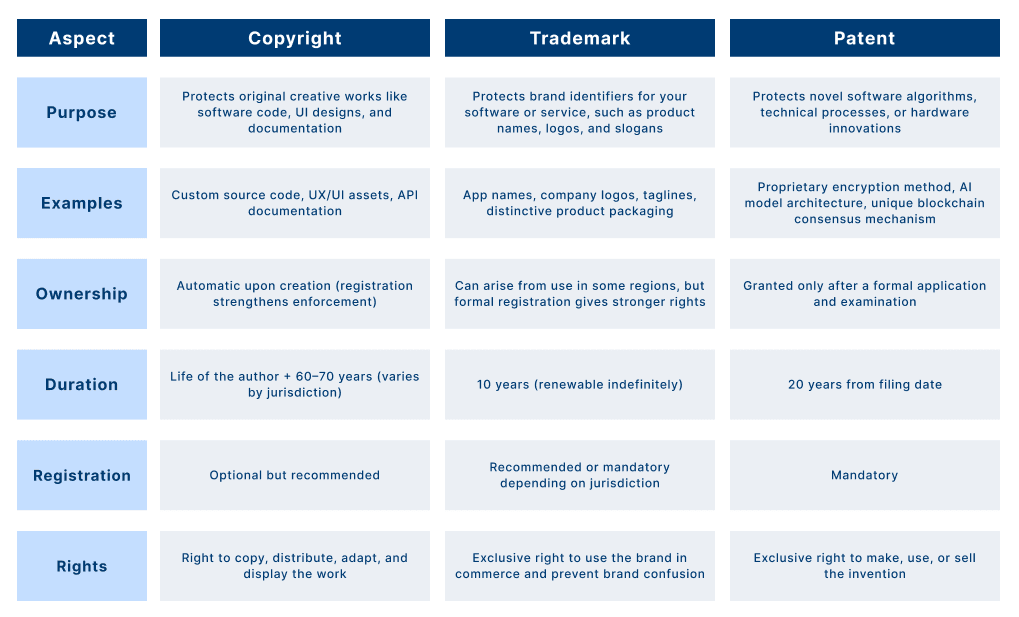
Failing to secure your intellectual property rights can have serious consequences for your business. It can result in brand dilution and a loss of market recognition, making it harder to stand out from competitors. Unauthorized use or reproduction of your work can erode your revenue streams, while stolen innovations can give rivals an unfair competitive advantage. In many cases, the absence of proper protection leads to costly legal disputes that drain valuable time, money, and resources, hindering business growth and innovation.
Intellectual property (IP) is one of the most valuable assets for any business, but protecting it requires more than just technical safeguards. Legal agreements play a crucial role in ensuring that ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality of IP are clearly defined and enforceable. By combining IP protection strategies with well-drafted agreements such as NDAs, IP rights contracts, and non-compete clauses, businesses can secure their innovations against misuse and establish a strong foundation for trust and compliance.
Watch full video on Legal agreement.*
Q1. Can a product have all three types of protections?
Yes. A product can have copyright for its creative content, a trademark for its brand name, and a patent for its invention.
Q2. What is the main difference between Copyright vs Trademark vs Patent?
Copyright protects creative works, trademark secures brand identifiers, and patent safeguards inventions. Think of it as protecting your art, your brand, and your innovations, each with its own rules and benefits.
Q3. How long does a patent take to secure?
It can take 1 to 3 years depending on jurisdiction and complexity.
Q4. What are the 4 types of intellectual property?
The four main types are patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, protecting inventions, brand identities, creative works, and confidential business information.
Q5. Can trademark rights be lost?
Yes, if the mark is not used or the registration is not renewed.
Understanding the distinctions between Copyright vs Trademark vs Patent ensures you apply the right protection for your assets. With the right IP protection, you can prevent unauthorized use, protect your market share, and strengthen your brand's credibility. It's not just about legal security, it's about protecting your reputation, your hard work, and your future.
So, take a moment to look at what makes your business special and make sure it's protected. Because in business, the smartest move isn't just creating something amazing-it's keeping it yours.
At Oodles, we help businesses safeguard their intellectual property through airtight legal agreements, strategic IP consulting, and technology-driven protection measures. Whether you need copyright registration, trademark enforcement, or patent guidance, our experts ensure your innovations remain protected.
Contact us now and secure your business assets today.